Based on a given scenario, administer and manage Nutanix data protection solutions
Data Protection Strategy
The below image is a representation of the capabilities that the Nutanix solution offers across the entire data protection spectrum.

Nutanix offers a natively integrated solution for data protection and continuous availability at VM granularity. It gives administrators an affordable range of options to meet the recovery point objectives (RPO) and recovery time objectives (RTO) for different applications.
Nutanix has options for:
- Integrated Local and Remote Snapshots
- Cloning and Recovery from Snapshots
- Cloud Connect for backup to AWS/ Azure
- Metro Availability and Async Replication
- Integration with 3rd part backup and Extensible APIs
Time Stream
Local snapshots placed on the same cluster as the source VM. The system creates a read only zero-space clone of the metadata, and marks the VM data immutable.
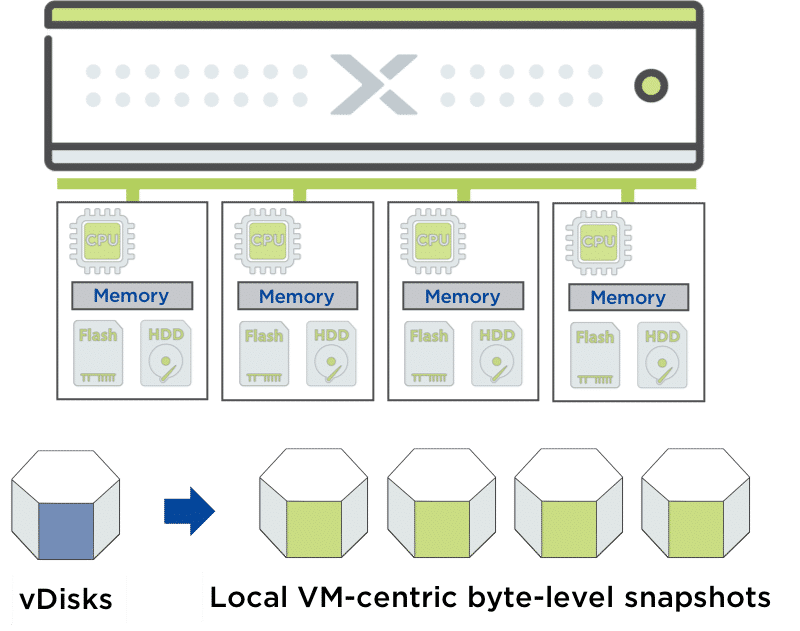
Use Cases
- Protection from Guest-OS corruption
- Snapshot VM environment
- Self-service file-level restore
Asynchronous Replication
Replication between Nutanix clusters. Only byte-level changes between snapshots of individual VM’s are sent over the network to the remote cluster.
Enables another host other than the one serving the I/O on the active virtual disk of the cluster to do the work of, eliminating bottlenecks.
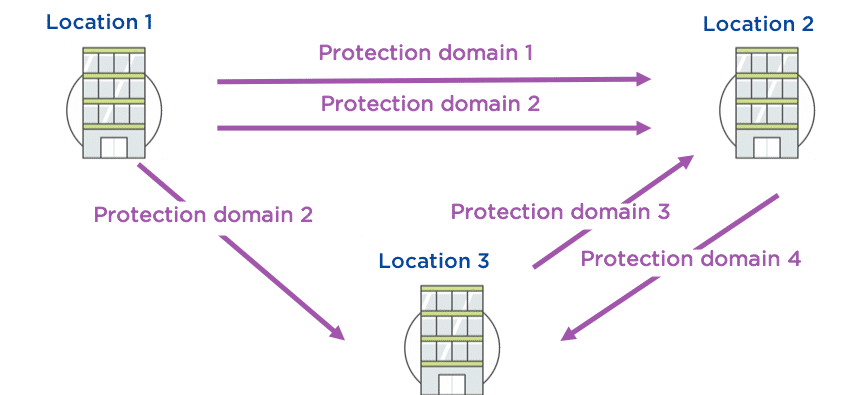
Use Cases
- Protection from VM corruption and deletion
- Protection from total site failure
NearSync
No restrictions on latency or distance.
Building upon the traditional asynchronous replication capabilities mentioned previously; Nutanix has introduced support for near synchronous replication (NearSync).
NearSync provides the best of both worlds: zero impact to primary I/O latency in addition to a very low RPO (one minute minimum). This allows users have a very low RPO without having the overhead of requiring synchronous replication for writes.
This capability uses a new snapshot technology called light-weight snapshot (LWS). Unlike the traditional vDisk based snapshots used by async, this leverages markers and is completely OpLog (SSD) based (vs. vDisk snapshots which are done in the Extent Store).
Hydration Point is the time at which Remote Site consolidates LWS into snapshots On a regular basis (hydration point), these changes (LWS) will be consolidated into a regular snapshot on the remote cluster. LWS resides in the Oplog which is carved out of the SSDs. Hydration removes LWS from the Oplog and thus frees up SSD resources.
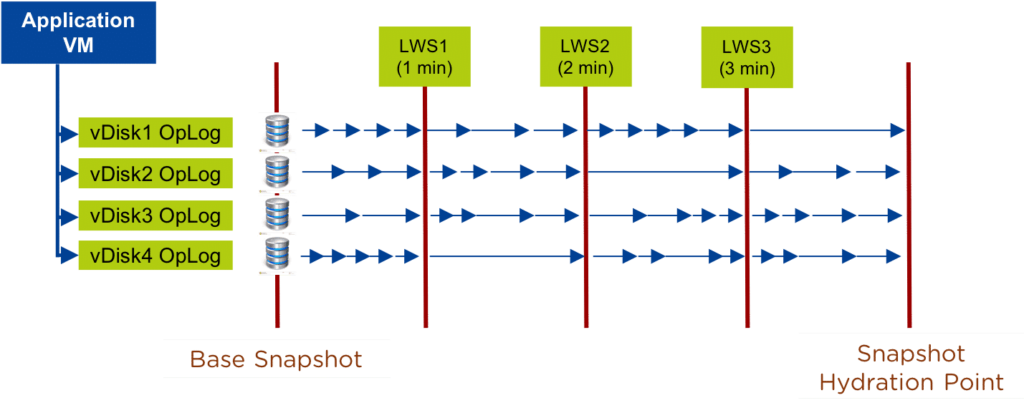
When a user configures a snapshot frequency <= 15 minutes, NearSync is automatically leveraged. Upon this, an initial seed snapshot is taken then replicated to the remote site(s). Once this completes in < 60 minutes (can be the first or n later), another seed snapshot is immediately taken and replicated in addition to LWS snapshot replication starting. Once the second seed snapshot finishes replication, all already replicated LWS snapshots become valid and the system is in stable NearSync.
In the event NearSync falls out of sync (e.g. network outage, WAN latency, etc.) causing the LWS replication to take > 60 minutes, the system will automatically switch back to vDisk based snapshots. When one of these completes in < 60 minutes, the system will take another snapshot immediately as well as start replicating LWS. Once the full snapshot completes, the LWS snapshots become valid and the system is in stable NearSync. This process is similar to the initial enabling of NearSync.
Requirements
- NearSync requires more SSD resources for storing snapshot date. Each SSD should be 1.2TB (1.92TB recommended)
- Both local and remote clusters must have 3 or more nodes
- All nodes should not have more than 40TB of capacity
- Support for 1-1 replication only
- Supports AHV and ESXi only.
Limitations
- There cannot be more than 10 entities in a NearSync PD
- Does not work with Async DR nor Metro
- Cannot add or remove once a NearSync PD is created
- Does not support AFS
- Does not support on-demand snapshot
- Does not support application consistent snapshot
- Does not support SSR
- Does not support multi-hypervisor cluster
More information on NearSync here.
Synchronous Replication (Metro Availability)
Synchronous Replication is a feature through which data is synchronously replicated between two sites in metro availability configuration. In an event of a disaster on any one site, real-time data is available on the other site.
- Requires <=5ms latency
- Compute spans two locations with access to shared pool of storage (stretch clustering)
- Near zero RTO
- Zero RPO
- Container names MUST be the same on both sides
- Acknowledge writes
- If link failure, clusters will operate independently
- Once link is re-established, sites are resynchronized (deltas only)
- In the event of a site failure, an HA event will occur where the VM’s can be restarted on the other site.
- Failover process is manual
- Metro Witness can be configured which can automate failover
- If the Witness fails, synchronous replication will continue without disruption
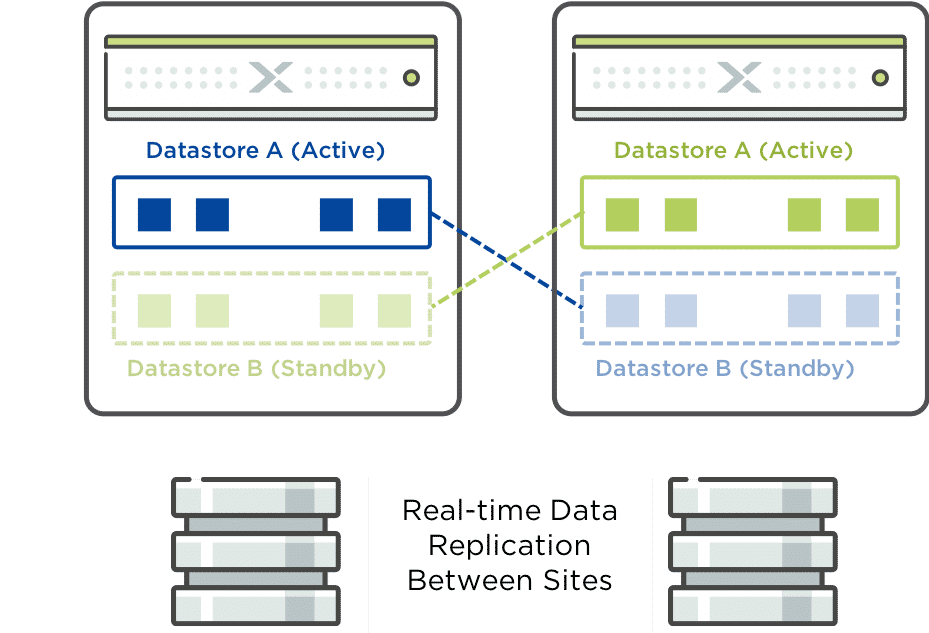
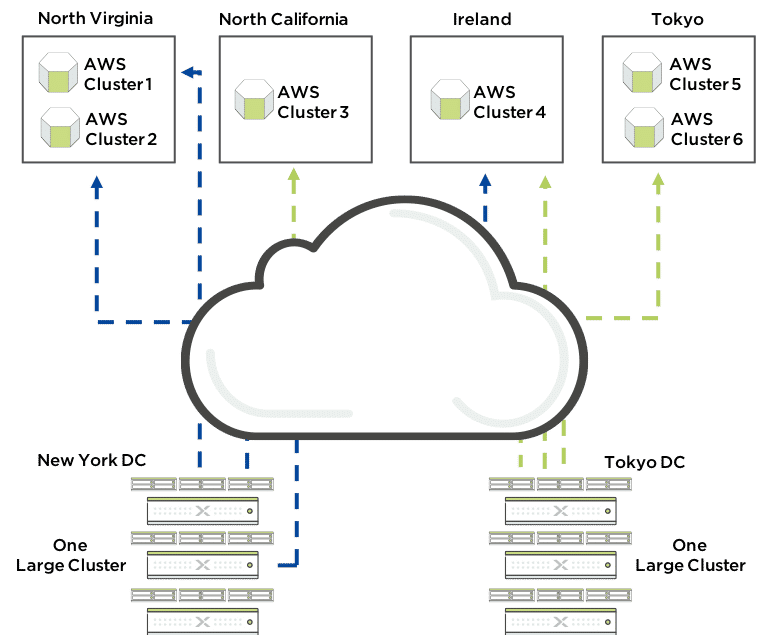
Cloud Connect
The Cloud Connect feature enables you to back up and restore copies of virtual machines and files to and from an on-premise cluster and a Nutanix Controller VM located on the Amazon Web Service (AWS) or Microsoft Azure cloud.
The AWS Remote Site is a single-node cluster which creates an m1.xlarge EC2 instance. A bucket is created in AWS S3 that can store up to 30 TB of data.
Currently, the Nutanix Cloud Connect feature enables you to configure D3 Azure Virtual Machines.
Use Cases
- Archiving
- Backup—not Disaster Recovery
VPC/VPN versus SSH
Only VPC/VPN-based Production Instances are supported for Security & Performance.
| Pros | Cons |
| Industry-standard secure transportation via IPSec VPN | Hardware VPN must be configured to connect to AWS VPN gateway |
| Prevents incoming traffic from outside world | Increased deployment complexity |
SSH-based instances can be used but are not supported for production due to performance reasons.
| Pros | Cons |
| Very easy, quick setup since no extra network changes are needed | Nutanix cluster accessible to the outside world using its public IP |
| Performance is lower due to SSH encryption/decryption | |
| Violates Backup SLAs |
More information on Cloud Connect here.
Single Node Replication Target
- Backup/DR for ROBO/SMB
- Support for AHV-only
- Up to 60TB Raw Capacity
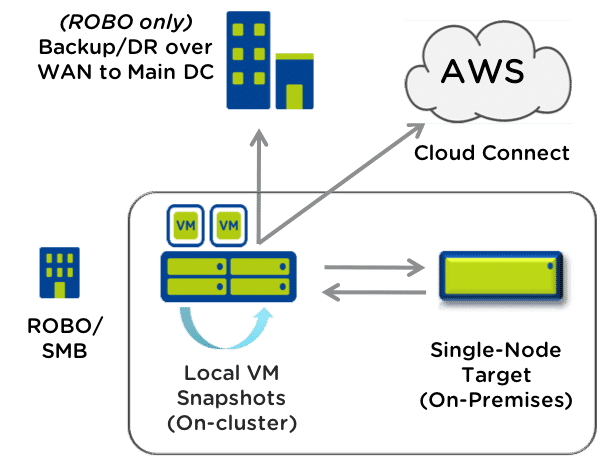
Use Cases
- Cost effective alternative to traditional options
- Self-service restore
- Supports compression/deduplication
Snapshots
Acropolis implements redirect-on-write, application-granular snapshots. When the system initially takes a snapshot of a VM or volume group, the system creates a read-only, zero space clone of the metadata. This method redirects any updates to existing protected data to a new location. None of the existing metadata or data in the snapshots needs to be copied or moved. As a result, ROW snapshots do not suffer the performance impact of the alternative, copy-on-write snapshot implementations.
Contrary to traditional approaches which require traversal of the snapshot chain (which can add read latency), each vDisk has its own block map. This eliminates any of the overhead normally seen by large snapshot chain depths and allows you to take continuous snapshots without any performance impact.
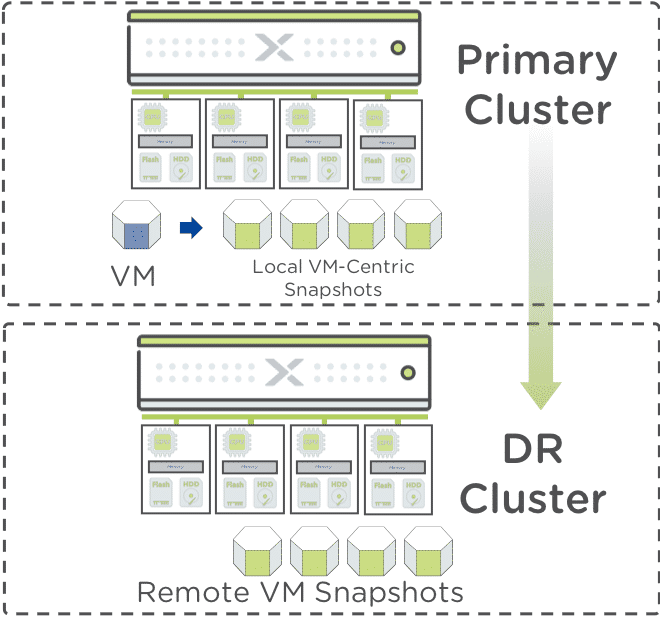
More information about Snapshots here.
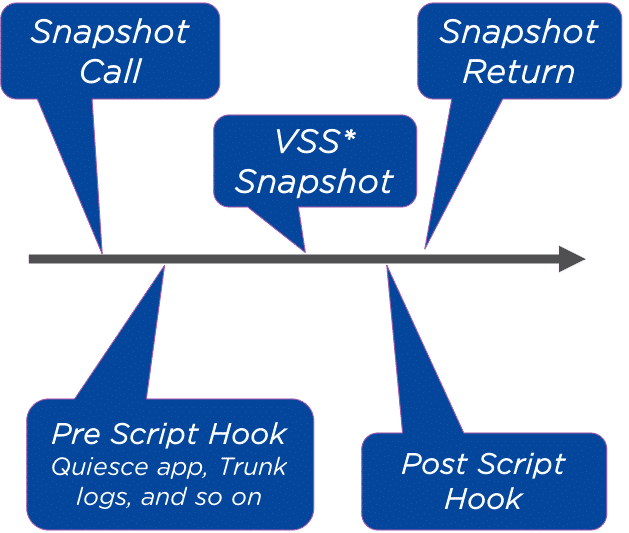
Application Consistent Snapshots
- Full application-aware snapshots for Windows and Linux
- Integrates with VSS on Windows
- Pre and postscript hooks available on Windows and Linux
- Hooks provide even deeper application integration
Third Party Backup Integration
- Commvault integration with AHV natively – without in-guest backup and restore agents
- Support for VMware vStorage API for Data Protection (VADP) and application-consistent snapshots using VSS helps your environment to work seamlessly with Symantec NetBackup, CommVault Simpana, Veeam, HYCU, and more.
- VM-level backup for Hyper-V using VSS for SMB Shares
- Support for NetBackup, Veeam and others with in-guest backup and restore agents
RPO and RTO considerations
- Time Stream and cloud: Used for high RPO and RTO which is in hours. It is used for minor incidents.
- Synchronous and asynchronous: Used for near-zero RPO and RTO. It is used for major incidents.