Describe AHV networking components and configuration settings
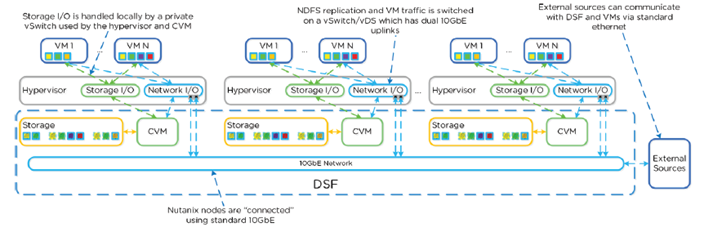
- No backplane for internode communication
- All I/O’s handled by hypervisor on private network
- I/O is forwarded from hypervisor to CVM
- CVM replicates with other nodes with external IP over public 10GB network
- Read requests are served locally
- Typically, the only traffic on the 10G public is replication
- Occasionally CVM will forward requests in event CVM is down or data is remote or for cluster tasks such as disk balancing
Recommended Network Configuration
| Network Component | Recommendations |
| Open vSwitch | Do not modify the OpenFlow tables that are associated with the default OVS bridge br0. |
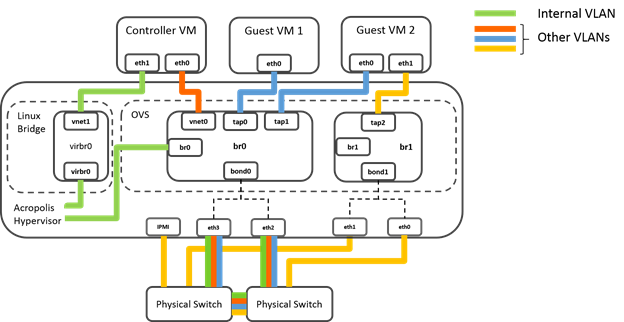
| VLANs | Add the Controller VM and AHV to the same VLAN. By default, the Controller VM and the hypervisor are assigned to VLAN 0, which effectively places them on the native VLAN configured on the upstream physical switch. Do not add any other device, including guest VMs, to the VLAN to which the Controller VM and hypervisor host are assigned. Isolate guest VMs on one or more separate VLANs. |
| Virtual bridges | Do not delete or rename OVS bridge br0.Do not modify the native Linux bridge virbr0. |
| OVS bonded port (bond0) | Aggregate the 10 GbE interfaces on the physical host to an OVS bond on the default OVS bridge br0 and trunk these interfaces on the physical switch. By default, the 10 GbE interfaces in the OVS bond operate in the recommended active-backup mode. |
| 1 GbE and 10 GbE interfaces (physical host) | If you want to use the 10 GbE interfaces for guest VM traffic, make sure that the guest VMs do not use the VLAN over which the Controller VM and hypervisor communicate. If you want to use the 1 GbE interfaces for guest VM connectivity, follow the hypervisor manufacturer’s switch port and networking configuration guidelines. Do not include the 1 GbE interfaces in the same bond as the 10 GbE interfaces. Also, to avoid loops, do not add the 1 GbE interfaces to bridge br0, either individually or in a second bond. Use them on other bridges. |
| IPMI port on the hypervisor host | Do not trunk switch ports that connect to the IPMI interface. Configure the switch ports as access ports for management simplicity. |
| Upstream physical switch | Nutanix does not recommend the use of Fabric Extenders (FEX) or similar technologies for production use cases. While initial, low-load implementations might run smoothly with such technologies, poor performance, VM lockups, and other issues might occur as implementations scale upward (see Knowledge Base article KB1612). Nutanix recommends the use of 10Gbps, line-rate, non-blocking switches with larger buffers for production workloads. Use an 802.3-2012 standards–compliant switch that has a low-latency, cut-through design and provides predictable, consistent traffic latency regardless of packet size, traffic pattern, or the features enabled on the 10 GbE interfaces. Port-to-port latency should be no higher than 2 microseconds. Use fast-convergence technologies (such as Cisco PortFast) on switch ports that are connected to the hypervisor host. Avoid using shared buffers for the 10 GbE ports. Use a dedicated buffer for each port. |
| Physical Network Layout | Use redundant top-of-rack switches in a traditional leaf-spine architecture. This simple, flat network design is well suited for a highly distributed, shared-nothing compute and storage architecture. Add all the nodes that belong to a given cluster to the same Layer-2 network segment. Other network layouts are supported as long as all other Nutanix recommendations are followed. |
| Controller VM | Do not remove the Controller VM from either the OVS bridge br0 or the native Linux bridge virbr0. |